Abstract
Introduction: Acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL) represents approximately 50% of all childhood cancers in Latin America. Mexico is not the exception. The impact of ALL survival on overall childhood cancer survival is significant. According to government data, five-year survival is about 52%. Mexico in Alliance with St. Jude (MAS) is a multi-site, intersectoral collaboration. The collaborative network has explored and reported on factors associated with this suboptimal outcome and have identified challenges with ALL risk group classification as a leading cause. For example, as many as 82% of children diagnosed with ALL in Mexico receive high-risk treatment and the tendency for higher-risk group assignment often occurs in response to limited access to cytogenetic testing and minimal residual disease (MRD) testing. This leads to higher intensity treatment and may explain the high rate of treatment-related death (TRD) (12%) documented during the induction but also subsequently. In our previous case series, only 75% of patients were alive at the end of the first year of treatment. These findings, led MAS to develop a consensus-derived standardized diagnosis and treatment schema (MAS-ALL18), which takes into account clinical, cytogenetic, and MRD results. Diagnostic testing is performed in a centralized laboratory. Although centred on delivery of standard of care, this experience represents is the first prospective multi-site cooperative group effort in Mexico. We report on early treatment (first 90 days) clinical and implementation outcomes utilizing the MAS-ALL18 adapted management guideline (AMG) in four member hospitals of the MAS collaboration network.
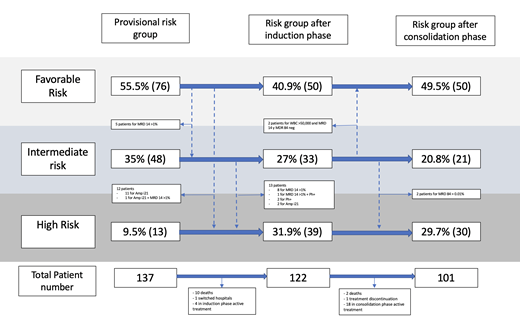
Results: From June 2019 to June 2020, 137 patients received treatment utilizing the MAS-ALL18 AMG in four publicly funded hospitals in Mexico. B-cell ALL represented 91.9% of the cases, 20.4% of patients were older than 9 years of age, 25.5% had a white blood cell count greater than 50,000 at diagnosis and 58.3% were male. Complete remission at the end of the induction was achieved in 90.6% of patients. TRD during the induction phase was 8%. MRD at Day 15 in 123 patients with B-cell ALL, 84.5% of them had MRD <1% and 7.3% had MRD ≥5%. MRD at Day 29 was assessed for the 10 patients diagnosed with T-cell ALL, 4 patients had MRD <0.01%, 2 had 0.02%, and 4 died during the induction phase. MRD was also assessed during consolidation (at Day 84) in 99 patients, 94.9% had MRD <0.01% and 5 patients MRD ≥0.01%, from which 3 had MRD at day 15 >1% and none registered an MRD result <0.5%. Utilizing the MAS-ALL18 risk group stratification, 50% of patients were assigned to a favorable risk group at the end of the consolidation. In 34 patients, the risk group was reclassified following the standardized algorithm; 30 reclassification events happened at the end of the induction and four at the end of the consolidation. Only two events were reassigned to a lower risk group, while the rest of the reclassifications were conducted to assign patients to a higher risk group due to unfavorable cytogenetics or an inadequate early response to treatment. High-risk treatment was ultimately assigned to 30% of patients using the MAS-ALL18 risk classification schema.
Conclusion: It is feasible to implement a standardized multi-site adapted management guideline for ALL risk group stratification and treatment allocation in Mexico in the context of a collaborative network. TRD remains high during the induction phase, nevertheless, this number shows an improvement (8%) compared to the 2015 data report (12%). The ALL risk group classification is transitioning from a rigid scheme that placed 80% of patients in a high-risk group to a dynamic classification system that considers cytogenetic testing and MRD conducted in a centralized and externally validated laboratory that serves as reference for all the participating hospitals. The standardized MAS-ALL18 approach allowed us to classify 50% of patients in a favorable risk group during and at the end of the induction phase, which implies receiving a lower intensity treatment with a high probability of cure and a lower risk of TRD. The implementation of MAS-ALL18 risk classification scheme reduced the number of children requiring high-risk treatment in the participating hospitals.
No relevant conflicts of interest to declare.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal